So far, the principal policy response to the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. mortgage market has been forbearance. On March 18, 2020, the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) directed the government-sponsored enterprises (GSE) Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to suspend foreclosures on single-family mortgages and start offering forbearance and modification plans to distressed borrowers.1
The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act, signed into law on March 27, codified the Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac forbearance programs, and included the government housing agency Ginnie Mae. The act directed the agencies to grant borrower requests for forbearance "with no additional documentation required other than the borrower's attestation to a financial hardship caused by the COVID-19 emergency..." In general, servicers of loans not covered by the law have set up similar forbearance programs.
What is mortgage forbearance?
Mortgage forbearance means a mortgage lender (that is, the holder of credit risk) allows a borrower to stop making mortgage payments for a fixed period of time. During that time, the lender does not charge late fees nor initiate foreclosure proceedings but does consider the borrower delinquent on the loan. Under normal circumstances, the lender would report the delinquency and the forbearance plan to credit bureaus. Under not-so-normal circumstances, including natural disasters, lenders often do not report loan status to credit bureaus. The CARES Act explicitly stipulates that forbearance resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic cannot negatively affect a borrower's credit score, so lenders cannot report borrowers in forbearance as being delinquent.
Once the forbearance period expires, the borrower has to make up the missed payments. For example, if the lender implements a six-month forbearance policy, then borrowers would be allowed to defer all payments for up to six months. After the forbearance period ends, the borrower and lender would typically negotiate a repayment plan that makes the lender whole in the long run but does not send the borrower back into distress. During this COVID-19 forbearance episode, Fannie, Freddie, and Ginnie Mae must provide borrowers affordable repayment options, such as converting the arrears into a partial claim, which is a non-interest-bearing second lien due at termination of the loan.
Forbearance is meant to provide short-term relief to financially distressed borrowers without inducing moral hazard by borrowers who do not need assistance. Since no debt is forgiven, the policy, in theory, should not appeal to borrowers who are not liquidity-constrained. Nevertheless, some empirical evidence indicates that some borrowers may be willing to engage in this "strategic forbearance."
While an acceptable exit strategy exists for borrowers, it is contingent on employment and income being restored before the forbearance period ends. For mortgage servicers, the magnitude of forbearance take-up is crucial to their liquidity—especially for nonbank servicers.
A liquidity squeeze arises because mortgage servicers must advance scheduled principal and interest payments to investors regardless of whether the borrower is paying. In addition, servicers must also pay tax and insurance payments.2 Either the borrower or guarantor will eventually reimburse the servicer, but in the short run, servicers must have sufficient liquidity to be able to bridge this gap. Such a squeeze is especially acute for nonbank servicers who not only are relatively thinly capitalized but also do not qualify for liquidity support programs that have been set up for banks. While this was a concern early in the pandemic, the GSEs and Ginne Mae have implemented polices that have helped to alleviate liquidity concerns of nonbank servicers.3
Forbearance take-up rate
In March, estimates of the fraction of households that would use forbearance in the coming months varied widely. On the one hand, optimists believed forbearance take-up would be fairly low because the CARES Act called for a generous increase in unemployment insurance benefits, which should provide many unemployed households with enough income to continue making payments. For example, FHFA director Mark Calabria estimated that only about 2 million GSE borrowers—a take-up rate of less than 5 percent—would seek forbearance.4
On the other hand, pessimists believed the numbers would be significantly higher. Laurie Goodman of the Urban Institute predicted that close to 12 percent, or 5.75 million borrowers, would request forbearance, and Mark Zandi of Moody's Analytics predicted that around 15 million households, or roughly 30 percent of mortgage borrowers, would miss payments.
To gauge the extent of forbearance, the Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) recently initiated a weekly Forbearance and Call Volume Survey of its members. The survey provides a lagged picture of forbearance rates. The latest survey covers more than three quarters of first-lien mortgages, so we believe it is representative of the overall market.
The earliest data from the survey indicate that as of March 8, 2020, the forbearance rate on all loans was below 1 percent, with both Ginnie Mae and Fannie/Freddie loans having forbearance rates of less than one quarter of 1 percent. Forbearance rates rose in the month of April, according to the survey (see the chart). On April 26, overall forbearance rates were at 7.55 percent, up by more than 480 basis points since the beginning of April. The rate of increase slowed in May, and the most recent survey (June 21) shows that the overall take-up percentage fell from the previous two weeks, going from 8.55 percent to 8.47 percent and marking the first decrease in the survey.
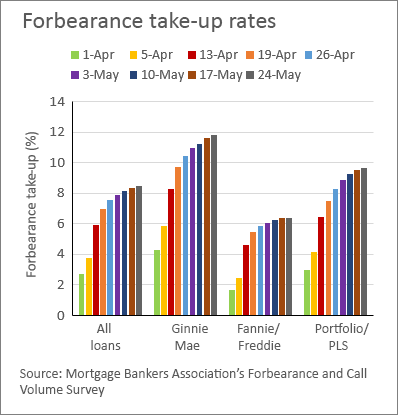
The data also indicate that there is significant heterogeneity across market segments. The rate for Ginnie Mae loans, 11.83 percent, has been flat for four weeks, while the rate for Fannie and Freddie loans, 6.26 percent, has fallen over the past three weeks. The rate for other loans—including those in private label securitizations (not government guaranteed) and held on portfolio—is 10.07 percent, which is essentially flat for the month of June. For Ginnie loans, this means an increase of more than 1,000 basis point since March 8.
Overall, the actual take-up rates are squarely between the optimistic and pessimistic forecasts.
Looking ahead
The forbearance take-up rates remain elevated, but recently, they have been flat or have fallen. This pattern is consistent with what we've seen in the labor markets—the rate of new unemployment claims has been fallen while the number of unemployed continues to be elevated. The generous increase in unemployment insurance benefits in the CARES Act certainly has helped take-up rates to be lower than the pessimistic forecasts. But the threat that forbearance will transition to foreclosure has regained power because the number of COVID-19 infections is increasing and the CARES Act unemployment insurance benefits will expire at the end of July.
1 [go back]
You can find the official press release on the FHFA website. On the same day, the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), in consultation with the federal government, implemented a 60-day moratorium on foreclosures and evictions for single-family homeowners with FHA-insured mortgages. In addition, HUD encouraged FHA mortgage servicers
to offer various loss-mitigation options to distressed borrowers. The options include short- and long-term forbearance options and mortgage modifications.
2 [go back] Servicers of agency loans are required to maintain first-lien status for the GSEs. This implies ensuring that the borrower has paid all property taxes, whether an escrow account exists or not, and that, in certain states, the borrower has met homeowner association commitments.
3 [go back]
On April 10, Ginnie Mae set up a lending facility that allows servicers experiencing liquidity issues to borrow funds to make forbearance-related principal-and interest advances. On April 21, the FHFA announced
that it would limit the requirements for servicers of Fannie and Freddie loans to forward principal-and-interest payments to investors to four months of forbearance.
4 [go back]
Calabria provided this estimate in an April 1, 2020, interview with CNBC ![]()
. In the same interview, he noted that about 300,000 GSE borrowers had already inquired about forbearance.